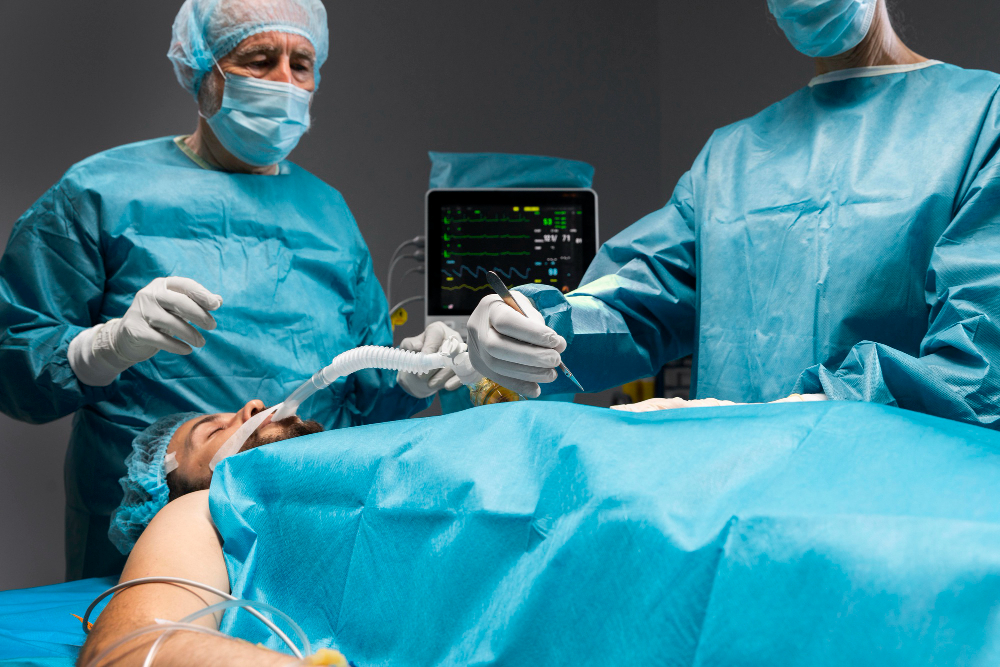
Laparoscopic Appendicectomy
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the appendix, a small finger-like part attached to the junction of the large intestine and small intestine that can become inflamed or infected, a condition known as appendicitis.
During the surgery, three small incisions around 5 to 10 mm are made in the abdomen, and a laparoscope, a small glass tube equipped with a camera, is inserted through one of the incisions. The surgeon then uses specialized instruments to remove the appendix through the other incisions.
Laparoscopic appendectomy is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, with a shorter recovery time and less scarring than traditional open surgery. Patients can usually go home the day after the surgery and can return to normal activities within a few days to a week.
Complications from laparoscopic appendectomy are rare but can include bleeding, infection, damage to nearby organs, and complications from anesthesia. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with our doctor before undergoing laparoscopic appendectomy.